AIRCRAFT GROUND HANDLING - ppt download

MOORING (TIEDOWN,PICKETING) Process of securing the aircraft against the weather condition during parking. Types. Normal tiedown procedure for normal weather. Heavy weather of storm condition tiedown procedure for storm weather.
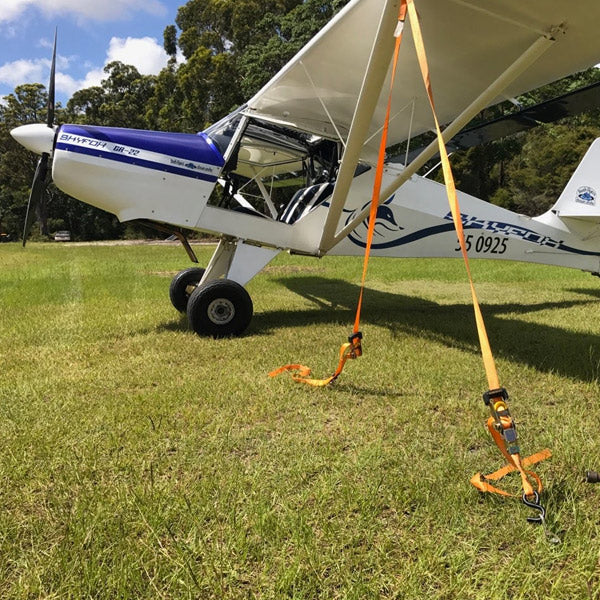
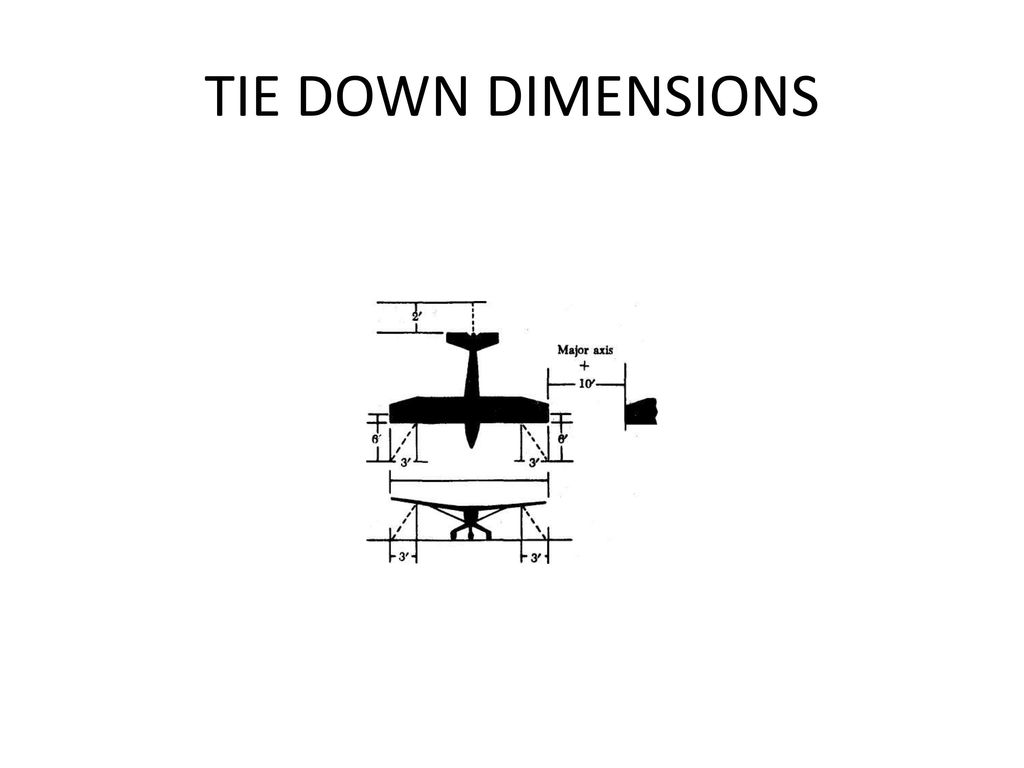
Small aircraft should be tied down after each flight. Aircraft should be parked against the wind direction (depends on the location of tie down points) Sufficient wing tip clearance should be given. Aircraft should be properly locked and all the wheels should be chocked properly.
All aircraft parking areas should be equipped for three-point tiedowns (pad eyes) Ring like fittings-They are normally set flush with the surface of the concrete or no more than one inch above it. More no of types are in use selected based on the type of surface.
Location of tiedowns is usually indicated by some means such as white or yellow paint markings or by surrounding the tiedpwn anchor with crushed stone. Tiedown anchors for small single-engine aircraft should provide a minimum holding power (strength) of approximately 3,000 pounds each.
Cable or chain tiedown is usually preferred for tying down large aircraft. Manila ropes should be inspected periodically. Nylon or Dacron tiedown ropes are preferable to manila rope.
Tiedown knots bowline knot
The chain-type tiedown sometimes is used as a better and stronger tiedown to secure the heaviest aircraft. This tiedown assembly is composed of an all metal quick-release mechanism, a tensioning device, and a length of chain with hooks.
Control surfaces should be locked. Light aircraft should be secured with ropes tied only at the aircraft tiedown rings provided for securing purposes. Rope should not be tied to a lift strut. Aircraft not equipped with tiedown fittings should be secured in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. Ropes should be tied to outer ends of struts on high-wing monoplanes. suitable rings should be provided where structural conditions permit, if the manufacturer has not already provided them.
The normal tiedown procedure for heavy aircraft can be accomplished with rope or cable tiedown. The number of such tiedowns should be determined based on weather conditions. Control surface locks which should be engaged or installed when the aircraft is secured. Common tiedown points.
Head airplane into prevailing wind whenever possible. Install control locks, all covers and guards. Chock all wheels fore and aft. Attach tiedown reels to airplane tiedown loops and to tiedown anchors or picketing blocks. Use picketing blocks for temporary tiedown only.
The best protection against windstorm damage is, of course, to fly the aircraft out of the impending storm area when there is sufficient time. The next best protective measure is to secure the aircraft in a storm proof hangar or other suitable shelter. The remaining alternative is to assure that the aircraft is tied down securely. When securing aircraft, fasten all doors and windows properly to minimize damage inside the aircraft. Engine openings, Pitot-static tubes for both reciprocating and gas-turbine type should be covered to prevent entry of foreign matter.
Be prepared for the worst storm conditions. (pouring rain, acid gusty winds with intermittent sheets of water flowing across the runways, ramps, and parking areas, with perhaps no hangar facilities available). Responsible service crews should plan in advance by becoming familiar with their aircraft manufacturer s instructions for the following. Tiedown ropes. installation of tiedown rings for attachment of tiedown ropes. securing nosewheel type aircraft vs. tailwheel type aircraft. aircraft weights and relative wind velocities that would make varied tiedown procedures necessary for pending weather emergencies.
Partially disassembled aircraft which are outdoors should be hangared as soon as storm warnings are received. Whenever possible, fly aircraft out of anticipated storm danger zones. If possible, hangar the aircraft in a stormproof hangar. Observe the minimum recommended strength for tiedown ropes. Place sand bags or spoiler boards to reduce the lifting tendency of the aircraft. (should not be overloaded)
Another means for tying down light aircraft (of various types and sizes) utilizes continuous lengths of parallel wire ropes passed through U-bolt anchors secured to ground. Tiedown points and Tiedown chains are attached to the wire rope with round-pin galvanized anchor shackles. This allows tiedown chains to float along wire rope and gives a Variable distance between anchor points so that a variety of aircraft can use a vertical tiedown without loss of space.
cont…. Wire rope tiedown line using vertical anchor chain
Multiengine aircraft will obviously require stronger tiedown facilities because of the additional weight of these aircraft. Anchor holding power of 4,000 pounds each required for lighter executive twin-engine aircraft. Do not depend on the weight of the multiengine aircraft to protect it from damage by windstorms. It is possible for a sudden, severe windstorm to move, damage, or even overturn such aircraft.
Gust locks should be used to protect control surfaces . If the landing gear uses down lock safety pins, these pins should be inserted at the time the aircraft is being secured.
When possible, helicopters should be secured in hangars. If not, they should be tied down securely. Refer maintenance manual for mooring procedure for a particular helicopter. Wheel chocks, control locks, rope tiedowns, mooring covers, tip socks, tiedown assemblies, parking brakes, and rotor brakes should be used to secure helicopters.
Spot the helicopter slightly more than rotor-span distance from other aircraft. Place wheel chocks ahead of and behind all wheels (where applicable). On helicopters equipped with skids, retract the handling wheels, lower the helicopter to rest on the skids, and install wheel position lock pins. Install a tiedown assembly on the end of the blade and align the blade over the tail boom. Secure the tiedown straps under the structural tubes of the tail boom. Tie the straps snugly without strain. During wet weather, provide some slack to avoid the possibility of the straps tightening.
cont… Fasten the tiedown ropes or cables to the forward and aft landing gear cross tubes and secure to ground stakes or tiedown rings.
AIRCRAFT GROUND HANDLING - ppt download

Ground Handling

PPT - Airport Services Offered by Transworld Aviation Zanzibar

Aircraft Ground Handling Equipment and Procedures

IATA - Top Ways to Safely Improve the Efficiency of Aircraft

Aviation and Ground Operations Safety: Strategies for a Smooth

AIRCRAFT HANDLING Part 2 Ground Handling. - ppt video online download

AIRCRAFT GROUND HANDLING - ppt download

Aircraft Handling and Flying Techniques LO1, PDF

Aircraft Ground Handling Equipment and Procedures

Aviation PowerPoint templates, Slides and Graphics

Get This Airport PowerPoint And Google Slides Template

AIRCRAFT GROUND HANDLING - ppt download

Airport Baggage Handling Systems - Jervis B. Webb Company

Ground Handling







