Biodiversity Variety of the earth's species, the genes they contain, the ecosystems in which they live, and the ecosystem processes such as energy flow. - ppt download

Red lists ICUN – International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources Published list of threatened species www. iucnredlist.org
Biodiversity Variety of the earth’s species, the genes they contain, the ecosystems in which they live, and the ecosystem processes such as energy flow.
Variety of the earth’s species, the genes they contain, the ecosystems in which they live, and the ecosystem processes such as energy flow and nutrient cycling that sustain all life.
Stable or increasing populations.
The Aye-Aye is a near-threatened species.
Population trend is typically decreasing. A recovering species can also be vulnerable. Good news! The Giant Panda is no longer endangered!
African Penguins are endangered due to decreasing habitat and frequent oil spills.
Species will likely go extinct soon if no action is taken.
K-strategists. Specialists. Tertiary consumers. Fixed migratory patterns. Narrow distribution. Commercially valuable. Large territories.
Background extinction – low rate of extinctions. Mass extinction-high rate of extinctions due to specific cause. Climate change.
The current extinction rate is increasing at an alarming rate due to human activities.
Causes include: HIPPO C. Habitat Destruction. Invasive species. Population Growth. Pollution. Over-harvesting. Climate Change.
A hotspot is an area where there are many threatened and endangered species. There are currently 34 hotspots in the world today.
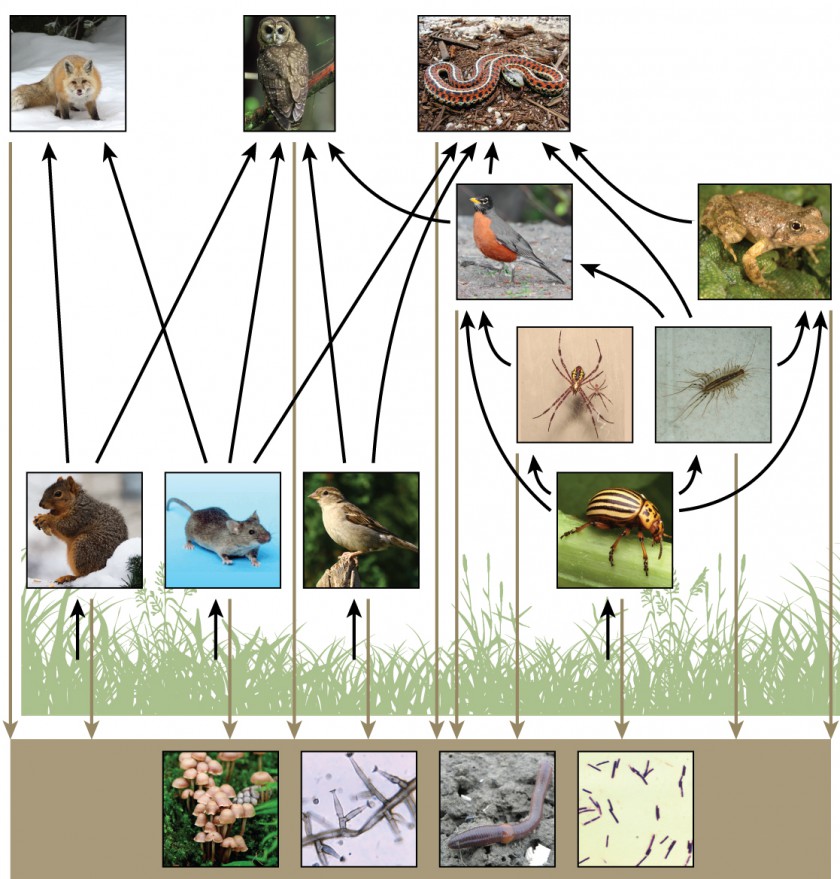
Ecological diversity – number of ecosystems in an area. Functional diversity – number of tropic levels. Genetic diversity – variety of genetic material within a species.
Explains how life has evolved from a common ancestor.
Organisms suited for the environment will survive to reproduce, thus passing down desirable traits. Examples: Giraffes. Camels. Influenza virus. Venus fly trap. NOTE – fittest does not equal strongest!!!
Location (rainforest vs. tundra) Continental movement- earthquakes and volcanoes. Climate change- cyclic cooling and heating of the earth. Catastrophic events- asteroid impacts, tsunamis, hurricanes, floods.
Two Phases. 1. Geographic isolation. A population is removed from others of it’s species for a long period of time. 2. Reproductive isolation. The removed population becomes so genetically different over time that it can no longer interbreed with others of it’s species.
Figure 4.5. Geological processes and biological evolution. Over millions of years the earth’s continents have moved very slowly on several gigantic tectonic plates. This process plays a role in the extinction of species as land areas split apart and promote the rise of new species when once isolated land areas combine. Rock and fossil evidence indicates that 200–250 million years ago all of the earth’s present-day continents were locked together in a supercontinent called Pangaea (top left). About 180 million years ago, Pangaea began splitting apart as the earth’s huge plates separated and eventually resulted in today’s locations of the continents (bottom right). 65 million years ago. Present. Fig. 4-5, p. 88.
Species diversity = species richness – the number of different species in a community. Species evenness – the abundance of species in a community.
Higher species richness = higher productivity = higher sustainability. Reasons: More likely to withstand droughts, disease, climate change, nutrient shortages. Higher number of producers lead to a higher biomass which leads to more carbon and nitrogen cycling.
Case Study: The Whooping Crane
In 1941 there were an estimated 14 whooping cranes left in the wild. The decline in this species was a major factor leading up to the creation of the Endangered Species Act.
Ex-situ conservation: Conservation outside of the natural habitat. In-situ conservation: Conservation in the natural habitat. A combination of techniques was used to save the Whooping Crane.
Established in Overseen by the US Fish and Wildlife Service. Penalties of violating the act: Funded by US taxes and penalty money.
prohibits unauthorized taking, possession, sale, and transport of endangered species; provides authority to acquire land for the conservation of listed species, using land and water conservation funds; authorizes establishment of cooperative agreements and grants-in-aid to States that establish and maintain active and adequate programs for endangered and threatened wildlife and plants; authorizes the assessment of civil and criminal penalties for violating the Act or regulations; and. authorizes the payment of rewards to anyone furnishing information leading to arrest and conviction for any violation of the Act or any regulation issued thereunder.
Biodiversity hotspots in relation to the largest concentrations of rare and potentially endangered species in the U.S. Figure
Is a voluntary agreement among participating countries to stop the trade of listed species. 180 countries participate: 5,600 animal species and 30,000 animals are protected under this act.
Habitat fragmentation is when an ecosystem is divided by a highway, neighborhood, buildings or other structures/land uses. Leads to: Decreased genetic diversity. Loss of habitat. Loss of breeding grounds. May disrupt migration patterns. Disruption of food chains.
Protect the land – National & State Parks and Forests. Introduce breeding programs and wildlife release to increase genetic diversity. Build Wildlife Cooridors.
Source: ourcollectivegood.com.
Wildlife Corridors in Colorado
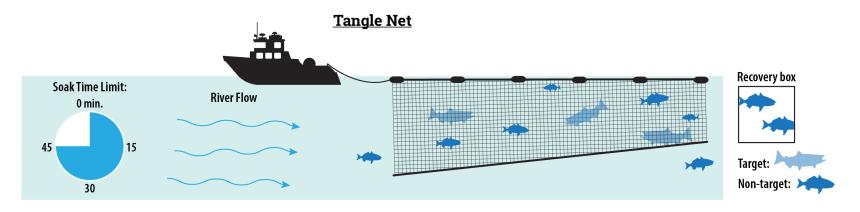
The major decline in the worldwide catch of fish since 1990 is because of over-fishing. By-catch- fish or animals that were not meant to be caught.
About 75% of the world’s commercially valuable marine fish species are over fished or fished near their sustainable limits. Big fish are becoming scarce. Smaller fish are next. We throw away 30% of the fish we catch. We needlessly kill sea mammals and birds.
Trawler fishing. Fish farming in cage. Spotter airplane. Sonar. Purse-seine fishing. Trawl flap. Trawl lines. Fish school. Trawl bag. Drift-net fishing. Long line fishing. Float. Buoy. Figure 12.A. Natural capital degradation: major commercial fishing methods used to harvest various marine species. These methods have become so effective that many fish species have become commercially extinct. Lines with hooks. Deep sea aquaculture cage. Fish caught by gills. Fig. 12-A, p
Drags a funnel shaped net along the ocean floor, weighted down with chains or metal plates. Some nets are large enough to hold 12 jumbo jets!!
Purse Seines Purse Seine Example
Tuna is a fish typically caught in purse seines. Dolphins are a by-catch of purse seines.
Lines are put out that can be up to 80 miles long w/ thousands of baited hooks on them. These are left out free-floating for days and then the boat comes back and picks them up. Pilot whales, dolphins, sea turtles, and birds are by-catch of this technique.
Anything that comes into contact w/ these nearly invisible nets are entangled. This leads to overfishing. Many unwanted fish and marine mammals, turtles and seabirds are caught.
Marine and mammal protection act - provides for protection and conservation of marine mammals. Magnuson Act- Sets quotas, size limits and seasons for fishing. UN Law of the Seas – allows countries to establish fishing quotas. Marine Sanctuaries Act- provides protected habitat for marine organisms.

PPT - Biodiversity PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:5374468

SOLUTION: Ap environmental science chapter 4 biodiversity and evolution pettit posts exam - Studypool

Sensors, Free Full-Text
17.1 Energy Flow through Ecosystems – Biology and the Citizen

Biodiversity
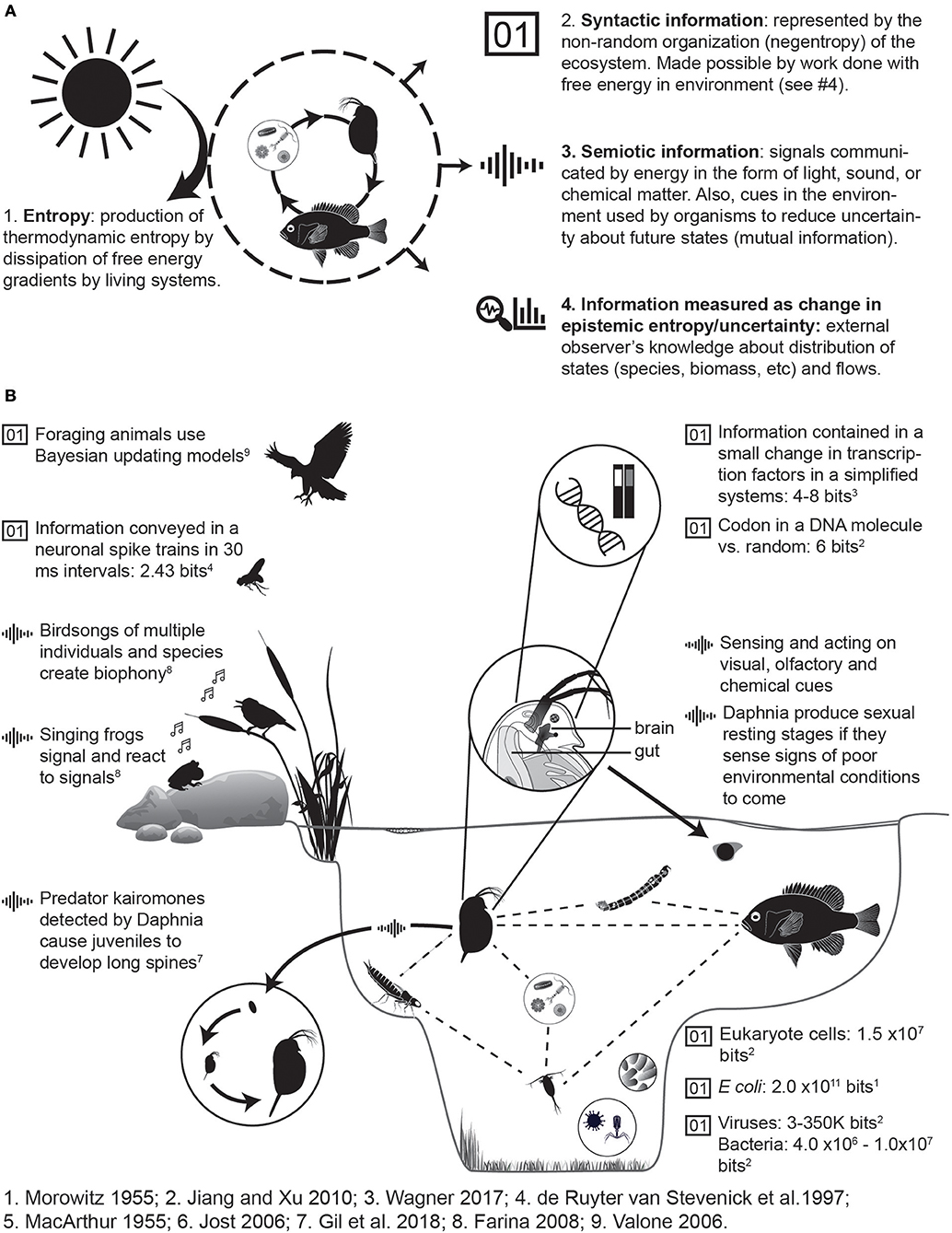
Frontiers Principles of Ecology Revisited: Integrating Information and Ecological Theories for a More Unified Science
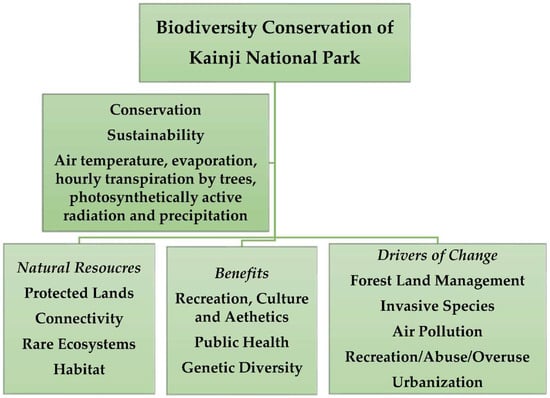
Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Understanding the Relationship Between Biodiversity, Evolution, and Ecology, PDF, Evolution

The impact of human activities and lifestyles on the interlinked microbiota and health of humans and of ecosystems - ScienceDirect

Biodiversity. The variety of Earth's species, the genes they contain, the ecosystems in which they live, & their functions in energy flow & nutrient cycling. - ppt download

Earth & Life Science, PDF, Ecosystem

PPT - Biodiversity and Evolution PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1561898

Unit 4 Chapters 4 and ppt download

Biodiversity - PowerPoint Slides - LearnPick India

Diversity, Free Full-Text